Hom bundle¶
This module implements the HomBundle class, for vector bundles constructed as homomorphism sheaves between two vector bundles.
The class inherits from the VectorBundle class, but sections, either local or global, are displayed as matrices.
EXAMPLES
sage: from vector_bundle import VectorBundle, trivial_bundle, savin_bundle
sage: F.<x> = FunctionField(GF(3))
sage: R.<y> = F[]
sage: K.<y> = F.extension(y^2 - x^5 - 1)
We construct a vector bundle of rank 2 and degree 4:
sage: F = VectorBundle(K, 3 * K.places_infinite()[0].divisor())
sage: F1 = VectorBundle(K, 2 * K.places_finite()[0].divisor())
sage: F2 = VectorBundle(K, 2 * K.places_finite()[1].divisor())
sage: V = savin_bundle(K, 2, 4, F, F1, F2); V.h0()
[(1, 0), (2*x, 1)]
We construct the HomBundle from 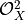 to
to V. Its global
sections should represent linear maps from 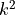 to
to 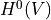 , where
, where 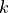 is the constant field of
is the constant field of 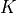 :
:
sage: domain = trivial_bundle(K).direct_sum_repeat(2)
sage: hom_bundle = domain.hom(V); hom_bundle.h0()
[
[1 0] [0 1] [2*x 0] [ 0 2*x]
[0 0], [0 0], [ 1 0], [ 0 1]
]
- class vector_bundle.hom_bundle.EndBundle(bundle)¶
Bases:
HomBundleVector bundles representing endomorphism sheaves of vector bundles.
EXAMPLES:
sage: from vector_bundle import trivial_bundle, canonical_bundle sage: F.<x> = FunctionField(GF(7)) sage: R.<y> = F[] sage: K.<y> = F.extension(y^4 - x^-2 - 1) sage: triv = trivial_bundle(K) sage: can = canonical_bundle(K) sage: triv.direct_sum(can).end() Endomorphism bundle of Vector bundle of rank 2 over Function field in y defined by y^4 + (6*x^2 + 6)/x^2
- global_algebra()¶
Return
self.h0()as a k-algebra in which computations may be done. Also return maps to and from the algebra.EXAMPLES:
sage: from vector_bundle import trivial_bundle, canonical_bundle sage: F.<x> = FunctionField(GF(7)) sage: R.<y> = F[] sage: K.<y> = F.extension(y^4 - x^-2 - 1) sage: triv = trivial_bundle(K) sage: can = canonical_bundle(K) sage: end = triv.direct_sum(can).end() sage: A, to_A, from_A = end.global_algebra(); A Finite-dimensional algebra of degree 4 over Finite Field of size 7 sage: h0 = end.h0()
- class vector_bundle.hom_bundle.HomBundle(domain, codomain)¶
Bases:
VectorBundleVector bundles representing homomorphism sheaves of vector bundles.
EXAMPLES
sage: from vector_bundle import VectorBundle sage: F.<x> = FunctionField(GF(3)) sage: R.<y> = F[] sage: K.<y> = F.extension(y^2 + x + 2) sage: ideals = [P.prime_ideal() for P in K.places_finite()[:2]] sage: g_finite = matrix([[1, x], [2, y]]) sage: g_infinite = matrix([[x, 1], [2, y]]) sage: V1 = VectorBundle(K, ideals, g_finite, g_infinite) sage: V2 = VectorBundle(K, K.places_infinite()[0].divisor()) sage: V = V1.hom(V2); V Homomorphism bundle from Vector bundle of rank 2 over Function field in y defined by y^2 + x + 2 to Vector bundle of rank 1 over Function field in y defined by y^2 + x + 2
- basis_finite()¶
Return basis of the finite lattice of the hom bundle.
OUTPUT:
The basis elements are represented as matrices.
EXAMPLES
sage: from vector_bundle import VectorBundle sage: F.<x> = FunctionField(GF(3)) sage: R.<y> = F[] sage: K.<y> = F.extension(y^2 + x + 2) sage: ideals = [P.prime_ideal() for P in K.places_finite()[:2]] sage: g_finite = matrix([[1, x], [2, y]]) sage: g_infinite = matrix([[x, 1], [2, y]]) sage: V1 = VectorBundle(K, ideals, g_finite, g_infinite) sage: O = K.maximal_order() sage: V2 = VectorBundle(K, K.places_finite()[2].prime_ideal(),1,x^2) sage: V = V1.hom(V2) sage: V.basis_finite() [[(x/(x^2 + x + 2))*y + (x + 2)/(x^2 + x + 2) (x/(x^2 + x + 2))*y + 2*x^2/(x^2 + x + 2)], [(2/(x^2 + x + 2))*y + x/(x^2 + x + 2) (2/(x^2 + x + 2))*y + x/(x^2 + x + 2)]]
- basis_infinite()¶
Return basis of the infinite lattice of the hom bundle.
OUTPUT:
The basis elements are represented as matrices.
EXAMPLES
sage: from vector_bundle import VectorBundle sage: F.<x> = FunctionField(GF(3)) sage: R.<y> = F[] sage: K.<y> = F.extension(y^2 + x + 2) sage: ideals = [P.prime_ideal() for P in K.places_finite()[:2]] sage: g_finite = matrix([[1, x], [2, y]]) sage: g_infinite = matrix([[x, 1],[2, y]]) sage: V1 = VectorBundle(K, ideals,g_finite,g_infinite) sage: O = K.maximal_order() sage: V2 = VectorBundle(K, K.places_finite()[2].prime_ideal(),1,x^2) sage: V = V1.hom(V2) sage: V.basis_infinite() [[(x^2/(x^3 + 2*x^2 + 1))*y + (x^4 + 2*x^3)/(x^3 + 2*x^2 + 1) (x^3/(x^3 + 2*x^2 + 1))*y + 2*x^2/(x^3 + 2*x^2 + 1)], [(2*x^3/(x^3 + 2*x^2 + 1))*y + x^2/(x^3 + 2*x^2 + 1) (2*x^4/(x^3 + 2*x^2 + 1))*y + x^3/(x^3 + 2*x^2 + 1)]]
- basis_local(place)¶
Return basis of the infinite lattice of the hom bundle.
OUTPUT:
The basis elements are represented as matrices.
EXAMPLES
sage: from vector_bundle import VectorBundle sage: F.<x> = FunctionField(GF(3)) sage: R.<y> = F[] sage: K.<y> = F.extension(y^2 + x + 2) sage: ideals = [P.prime_ideal() for P in K.places_finite()[:2]] sage: g_finite = matrix([[1,x],[2,y]]) sage: g_infinite = matrix([[x,1],[2,y]]) sage: V1 = VectorBundle(K, ideals,g_finite,g_infinite) sage: O = K.maximal_order() sage: V2 = VectorBundle(K, K.places_finite()[2].prime_ideal(),1,x^2) sage: V = V1.hom(V2) sage: place = K.places_finite()[0] sage: V.basis_local(place) [[(1/(x^2 + x + 2))*y + (x + 2)/(x^3 + x^2 + 2*x) (1/(x^2 + x + 2))*y + 2*x/(x^2 + x + 2)], [(2/(x^2 + x + 2))*y + x/(x^2 + x + 2) (2/(x^2 + x + 2))*y + x/(x^2 + x + 2)]] sage: all([all([(mat * g_finite)[0, j].valuation(place) >= (V2._ideals[0] * V1._ideals[j]**-1).divisor().valuation(place) for j in range(2)]) for mat in V.basis_local(place)]) True
- codomain()¶
Return the codomain of self
EXAMPLES
sage: from vector_bundle import VectorBundle sage: F.<x> = FunctionField(GF(3)) sage: L1 = VectorBundle(F, x.poles()[0].divisor()) sage: L2 = VectorBundle(F, x.zeros()[0].divisor()) sage: V = L1.hom(L2); V.codomain() == L2 True
- conorm(K)¶
Return the conorm of a hom bundle.
It is the same thing as the hom bundle of the conorms of its domain and codomain.
EXAMPLES
sage: from vector_bundle import VectorBundle sage: F.<x> = FunctionField(GF(3)) sage: R.<y> = F[] sage: K.<y> = F.extension(y^2 + x + 2) sage: ideals = [P.prime_ideal() for P in F.places_finite()[:2]] sage: g_finite = matrix([[1, x], [2, x]]) sage: g_infinite = matrix([[x, 1], [2, x]]) sage: V1 = VectorBundle(F, ideals, g_finite, g_infinite) sage: ideals = [P.prime_ideal() for P in F.places_finite()[1:3]] sage: g_finite = matrix([[0, x], [1, 1/x]]) sage: g_infinite = matrix([[x, 2*x^2], [2, 1]]) sage: V2 = VectorBundle(F, ideals, g_finite, g_infinite) sage: V1.conorm(K).hom(V2.conorm(K)) == V1.hom(V2).conorm(K) True
- coordinates_in_h0(mat)¶
Return the coordinates in the basis of
self.h0()of the matrixmatEXAMPLES:sage: from vector_bundle import trivial_bundle, canonical_bundle sage: F.<x> = FunctionField(GF(3)) sage: R.<y> = F[] sage: K.<y> = F.extension(y^4 - x^-2 - 1) sage: triv = trivial_bundle(K) sage: can = canonical_bundle(K) sage: V1 = triv.direct_sum(can) sage: V2 = can.direct_sum(triv) sage: hom = V1.hom(V2) sage: hom.coordinates_in_h0(matrix([[0, 1], [1, 0]])) (1, 1, 0, 0)
- domain()¶
Return the domain of self
EXAMPLES
sage: from vector_bundle import VectorBundle sage: F.<x> = FunctionField(GF(3)) sage: L1 = VectorBundle(F, x.poles()[0].divisor()) sage: L2 = VectorBundle(F, x.zeros()[0].divisor()) sage: V = L1.hom(L2); V.domain() == L1 True
- h0()¶
Returns the 0th cohomology group of the hom bundle. The global sections are output in matrix form, they are the global homomorphisms from
self._domaintoself._codomain.EXAMPLES
sage: from vector_bundle import VectorBundle sage: F.<x> = FunctionField(GF(3)) sage: R.<y> = F[] sage: K.<y> = F.extension(y^2 + x + 2) sage: ideals = [P.prime_ideal() for P in K.places_finite()[:2]] sage: g_finite = matrix([[1, x], [2, y]]) sage: g_infinite = matrix([[x, 1], [2, y]]) sage: V1 = VectorBundle(K, ideals, g_finite, g_infinite) sage: O = K.maximal_order() sage: V2 = VectorBundle(K, K.places_finite()[2].prime_ideal(),1,x^2) sage: V = V1.hom(V2) sage: h0 = V.h0(); len(h0) == V.degree() + (1-K.genus())*V.rank() True sage: all([all([(mat * g_finite)[0, j] in V2._ideals[0] * V1._ideals[j]**-1 for j in range(2)]) for mat in h0]) True sage: O_infinity = K.maximal_order_infinite() sage: all([all([a in O_infinity for a in (x**-2 * mat * g_infinite).list()]) for mat in h0]) True
- hom(other)¶
Return the Hom bundle from self to other.
If other is a vector bundle, this is the hom bundle from
self._codomaintoself._domain.tensor_product(other). If other is also a hom bundle, this is the hom bundle fromself.codomain().tensor_product(other.domain())toself.domain().tensor_product(other.codomain()EXAMPLES:
sage: from vector_bundle import VectorBundle sage: F.<x> = FunctionField(GF(7)) sage: L1 = VectorBundle(F, 2*x.zeros()[0].divisor()) sage: L2 = VectorBundle(F, -3*x.poles()[0].divisor()) sage: hom = L1.hom(L2) sage: T = L1.tensor_product(L2) sage: hom.hom(hom) == T.end() True
- image(f)¶
Return an image of global homomorphism
fwhich is an element of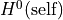 .
.That is, a vector bundle
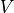 together with an injective morphism of
together with an injective morphism of 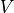 into
into self.codomainsuch that the image of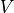 in
in self.codomainis also the image off.EXAMPLES
sage: from vector_bundle import trivial_bundle, canonical_bundle sage: F.<x> = FunctionField(GF(7)) sage: R.<y> = F[] sage: K.<y> = F.extension(y^2 - x^3 - x) sage: triv = trivial_bundle(K) sage: can = canonical_bundle(K) sage: V1 = triv.direct_sum(can) sage: V2 = can.direct_sum(triv) sage: hom = V1.hom(V2) sage: image, map = hom.image(matrix(K, [[0, 1], [0, 0]])) sage: image.isomorphism_to(can) is not None True sage: image.hom(V2).coordinates_in_h0(map) (1, 0)
- is_isomorphism(f)¶
Check if f is an isomorphism from
self.domain()toself.codomain()EXAMPLES:
sage: from vector_bundle import atiyah_bundle, canonical_bundle sage: F.<x> = FunctionField(GF(7)) sage: R.<y> = F[] sage: K.<y> = F.extension(y^2 - x^3 - x) sage: V = atiyah_bundle(K, 2, 0) sage: W = atiyah_bundle(K, 2, 0, canonical_bundle(K)) sage: isom = x^2/(x^2 + 3) * identity_matrix(K, 2) sage: V.hom(W).is_isomorphism(isom) True
- kernel(f)¶
Return a kernel of global homomorphism
fwhich is an element of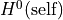 .
.That is, a vector bundle
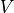 together with an injective morphism of
together with an injective morphism of 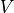 into
into self.domainsuch that the image of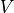 in
in self.domainis the kernel off.EXAMPLES
sage: from vector_bundle import trivial_bundle, canonical_bundle sage: F.<x> = FunctionField(GF(7)) sage: R.<y> = F[] sage: K.<y> = F.extension(y^2 - x^3 - x) sage: triv = trivial_bundle(K) sage: can = canonical_bundle(K) sage: V1 = triv.direct_sum(can) sage: V2 = can.direct_sum(triv) sage: hom = V1.hom(V2) sage: kernel, map = hom.kernel(matrix(K, [[0, 1], [0, 0]])) sage: kernel.isomorphism_to(triv) is not None True sage: kernel.hom(V1).coordinates_in_h0(map) (1, 0)
- tensor_product(other)¶
Return the tensor product of a hom bundle and a vector bundle. This is the same thing as
self._domain.hom(self._codomain.tensor_product(other))EXAMPLES:
sage: from vector_bundle import VectorBundle sage: F.<x> = FunctionField(GF(7)) sage: L1 = VectorBundle(F, 2*x.zeros()[0].divisor()) sage: L2 = VectorBundle(F, -3*x.poles()[0].divisor()) sage: hom = L1.hom(L2) sage: hom2 = L1.hom(L2.tensor_product(L1)) sage: hom.tensor_product(L1) == hom2 True