Ext group¶
This module implements the ExtGroup and ExtGroupElement classes used for building extensions of vector bundles.
AUTHORS:
_Mickaël Montessinos: initial implementation
- class vector_bundle.ext_group.ExtGroup(left, right, precompute_basis=False)¶
Bases:
SageObjectThe group of extensions of
leftbyright.The group
 is
is
 .
Its elements may be represented as matrices of infinite répartitions
lying in
.
Its elements may be represented as matrices of infinite répartitions
lying in  or as
vectors of length
or as
vectors of length self.dim()with coefficients in the coefficient field, representing linear forms on , where
, where
 is the canonical bundle of the function field of
is the canonical bundle of the function field of leftandrightThe two representations are related via Serre duality.If
precompute_basisis set toTrue, a basis of répartition matrices is computed. Its element represent the linear formsvector([0,...,0,1,0,...,0]). Otherwise, linear forms are converted to elements of the on the fly. You should set
on the fly. You should set precompute_basistoTrueonly if you plan to create several extensions with this group.INPUT:
left– VectorBundleright– VectorBundle; must have the same function field as leftprecompute_basis– boolean
EXAMPLES
sage: from vector_bundle import VectorBundle, trivial_bundle sage: F.<x> = FunctionField(GF(3)) sage: triv = trivial_bundle(F) sage: triv.extension_group(triv) Extension group of Vector bundle of rank 1 over Rational function field in x over Finite Field of size 3 by Vector bundle of rank 1 over Rational function field in x over Finite Field of size 3.
- basis()¶
Return a basis of
 group. Its element are matrices of
infinite répartitions represented by field elements.
group. Its element are matrices of
infinite répartitions represented by field elements.Computes and stores the basis if it was not precomputed yet.
EXAMPLES
sage: from vector_bundle import VectorBundle sage: F.<x> = FunctionField(GF(11)) sage: R.<y> = F[] sage: K.<y> = F.extension(y^2 - x^5 - 1) sage: ksi = VectorBundle(K, K.places_finite()[0].divisor()) sage: ext = ksi.extension_group(ksi.dual()); ext.basis() [[(x^9/(x^10 + 2*x^5 + 1))*y], [(x^3/(x^5 + 1))*y], [x^6/(x^5 + 1)]]
- dim()¶
Return the dimension of the extension group as a vector space over the base coefficient field
EXAMPLES
sage: from vector_bundle import VectorBundle sage: F.<x> = FunctionField(GF(11)) sage: R.<y> = F[] sage: K.<y> = F.extension(y^2 - x^5 - 1) sage: ksi = VectorBundle(K, K.places_finite()[0].divisor()) sage: ext = ksi.extension_group(ksi.dual()); ext.dim() 3
- dual_basis()¶
This is the same as
self.dual_bundle().h0()The output basis is dual toself.basis()under Serre duality.EXAMPLES
sage: from vector_bundle import VectorBundle sage: F.<x> = FunctionField(GF(11)) sage: R.<y> = F[] sage: K.<y> = F.extension(y^2 - x^5 - 1) sage: ksi = VectorBundle(K, K.places_finite()[0].divisor()) sage: ext = ksi.extension_group(ksi.dual()); ext.dual_basis() [[x^4/(x^5 + 6)], [x^5/(x^5 + 6)], [(x^2/(x^5 + 6))*y + 10*x^2/(x^5 + 6)]]
- dual_bundle()¶
Return the dual bundle of the
 bundle. This bundle
is
bundle. This bundle
is  , where
, where
 is a canonical line bundle of
is a canonical line bundle of 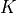 .
.EXAMPLES
sage: from vector_bundle import VectorBundle sage: F.<x> = FunctionField(GF(11)) sage: R.<y> = F[] sage: K.<y> = F.extension(y^2 - x^5 - 1) sage: ksi = VectorBundle(K, K.places_finite()[0].divisor()) sage: ext = ksi.extension_group(ksi.dual()); ext.dual_bundle() Homomorphism bundle from Vector bundle of rank 1 over Function field in y defined by y^2 + 10*x^5 + 10 to Vector bundle of rank 1 over Function field in y defined by y^2 + 10*x^5 + 10
- extension(ext=None)¶
Return the extension of
self.left()byself.right()encoded byext.extcan be a matrix of elements ofself._function_fieldwhich represents the constant value over the infinite places of a répartition matrix with support at infinity representing an element of .
Such an element encodes an extension
.
Such an element encodes an extension 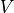 :
:

extcan also be a vector of length representing an
extension in the basis of the Ext vector space.
representing an
extension in the basis of the Ext vector space.By default,
extis chosen as any non trivial extension.EXAMPLES
sage: from vector_bundle import VectorBundle, trivial_bundle sage: F.<x> = FunctionField(GF(11)) sage: R.<y> = F[] sage: K.<y> = F.extension(y^2 - x^3 - x) sage: triv = trivial_bundle(K) sage: ext = triv.extension_group(triv) sage: V = ext.extension() sage: V.rank() 2 sage: V.determinant() == triv True sage: V.h0() [(1, 0)] sage: V.end().h0() [ [0 1] [1 0] [0 0], [0 1] ]
- left()¶
Return the left vector bundle of
self.EXAMPLES
sage: from vector_bundle import VectorBundle sage: F.<x> = FunctionField(GF(3)) sage: L1 = VectorBundle(F, x.zeros()[0].divisor()) sage: L2 = VectorBundle(F, x.poles()[0].divisor()) sage: ext = L1.extension_group(L2); ext.left() == L1 True
- right()¶
Return the right vector bundle of
self.EXAMPLES
sage: from vector_bundle import VectorBundle sage: F.<x> = FunctionField(GF(3)) sage: L1 = VectorBundle(F, x.zeros()[0].divisor()) sage: L2 = VectorBundle(F, x.poles()[0].divisor()) sage: ext = L1.extension_group(L2); ext.right() == L2 True